期刊:Chemosphere
主题:黑曲霉缓解铀毒促芋属植物生长的机制(钙信号)
标题:Aspergillus niger changes the chemical form of uranium to decrease its biotoxicity, restricts its movement in plant and increase the growth of Syngonium podophyllum
影响因子:4.427
监测指标:Ca2+流速
检测部位:合果芋(白蝴蝶)根部成熟区、黑曲霉菌丝
Ca2+流速流实验处理方法:
3.0 mg·L-1铀处理5min/24h Ca2+流速流实验测试液成份:
0.1mM CaCl2,pH 6.0
作者:南华大学王永东、邹超
英文摘要
Aspergillus niger (A. niger) and Syngonium podophyllum (S. podophyllum) have been used for wastewater treatment, and have exhibited a promising application in recent years.
To determine the effects of A. niger on uranium enrichment and uranium stress antagonism of S. podophyllum, the S. podophyllum-A. niger combined system was established, and hydroponic remediation experiments were carried out with uranium-containing wastewater.
The results revealed that the bioaugmentation of A. niger could increase the biomass of S. podophyllum by 5–7%, reverse the process of U(VI) reduction induced by S. podophyllum, and increase the bioconcentration factor (BCF) and translocation factor (TF) of S. podophyllum to uranium by 35–41 and 0.01–0.06, respectively, thereby improving the reduction of uranium in wastewater.
Moreover, A. niger could promote the cell wall immobilization and the subcellular compartmentalization of uranium in the root of S. podophyllum, reduce the phytotoxicity of uranium entering root cells, and inhibit the calcium efflux from root cells, thereby withdrawing the stress of uranium on S. podophyllum.
中文摘要(谷歌机翻)
黑曲霉(A.niger)和Syngonium podophyllum(S.potophyllum)已经用于废水处理,并且近年来已经展现出有希望的应用。
为了确定黑曲霉对S. podophyllum,S。podophyllum-A的铀浓缩和铀胁迫拮抗作用。建立了尼日尔联合系统,并对含铀废水进行了水培修复试验。
结果表明,黑曲霉的生物强化可以使S. podophyllum的生物量增加5-7%,逆转S. podophyllum诱导的U(VI)还原过程,提高生物富集因子(BCF)和转运因子。 (TF)S. podophyllum分别为35-41和0.01-0.06的铀,从而改善了废水中铀的还原。
此外,黑曲霉可促进S. podophyllum根部细胞壁的固定化和铀的亚细胞区室化,降低铀进入根细胞的植物毒性,抑制根细胞的钙外流,从而消除铀的压力。 S. podophyllum。
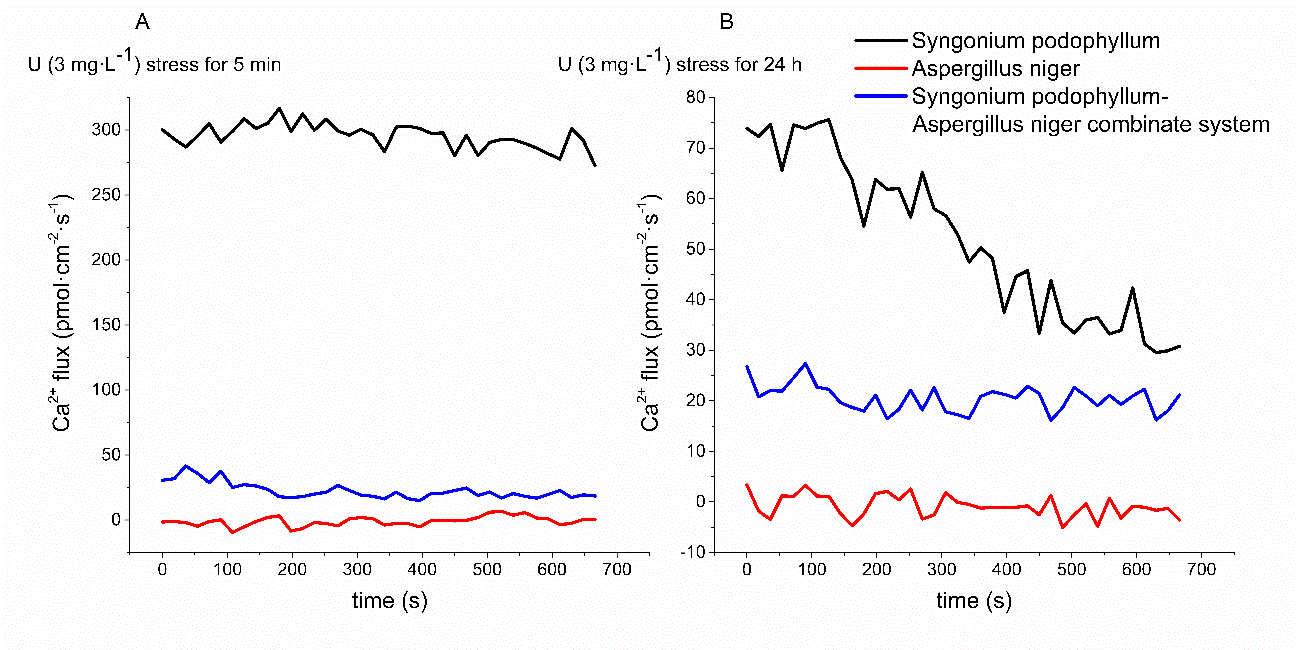
结果表明:在图中,黑曲霉的钙离子流速维持在约0pmol·cm-2·s-1,这表明在3.0mg·L-1铀胁迫下,Ca2+浓度梯度在黑曲霉细胞保持平衡,其正常生长不受抑制。
加入3.0mg·L-1的铀溶液5min后(图A),对照组的白蝴蝶根细胞的钙离子外排约为300pmol·cm-2·s-1。这表明在铀胁迫下,白蝴蝶根细胞中Ca2+浓度梯度被破坏,其正常生长受到抑制。钙离子的外排也发生在治疗组中。然而,与对照组相比,外排率显着下降,达到42pmol·cm-2·s-1以下,且持续下降。然后,最终稳定在约20pmol·cm-2·s-1。这表明黑曲霉可以抑制白蝴蝶根细胞的钙外流,从而减弱白蝴蝶生长中铀的毒性。
用3.0mg·L-1的铀胁迫处理24h后(图B),对照组根系的钙外排速率降至76 pmol·cm-2·s-1以下,并呈现持续下降趋势。最后保持在约30pmol·cm-2·s-1。这可能是因为白蝴蝶的自我调节以减弱铀的植物毒性。处理组根细胞的钙离子外排速率维持在20pmol·cm-2·s-1。这反映出黑曲霉抑制白蝴蝶根细胞钙外排的作用可持续很长时间。
旭月版权所有,转载注明出处
